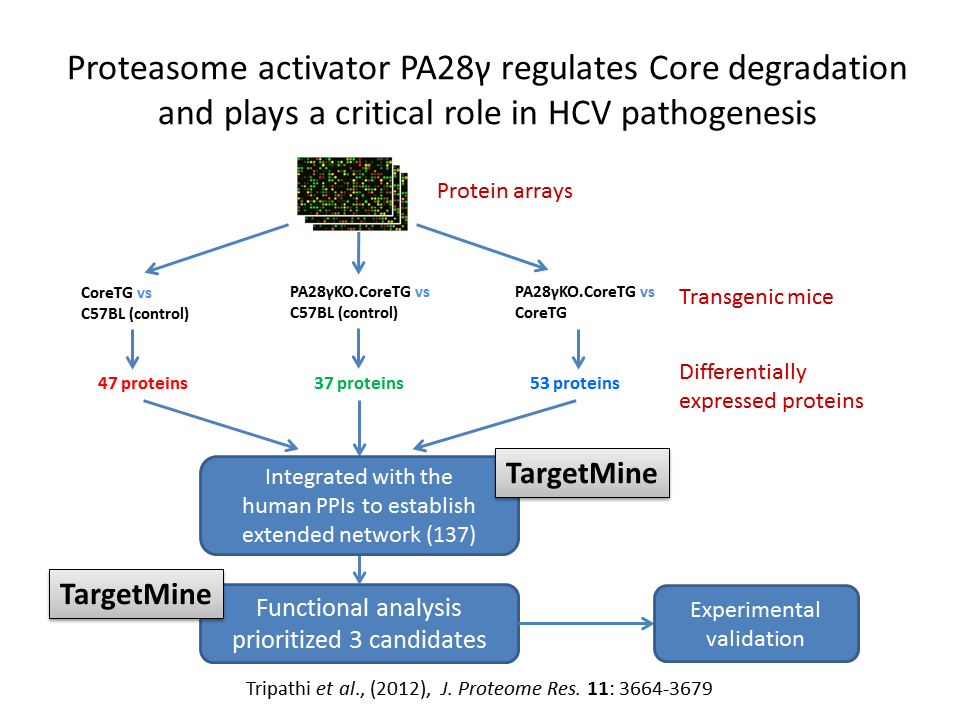
 Proteasome activator PA28γ regulates Core degradation and plays a critical role in HCV pathogenesis and is thus, a promising target for anti-HCV therapies. Suppressed PA28γ expression in transgenic mice expressing Core in the liver, impairs HCV pathogenesis. However, a precise understanding of the role of PA28γ in HCV pathogenesis remains unclear. In order to study the role of PA28γ involving in the biological network, differentially expressed genes by comparing Core transgenic mice with or without the knockout of PA28γ expression against the wild type (WT) samples were identified using protein array. The differentially expressed proteins were then integrated with the human PPIs to establish extended PPI networks using TargetMine. TargetMine was also employed for functional analysis of the inferred PPI networks to identify cellular processes targeted by Core and PA28γ in HCV pathology and prioritize candidates for further experimental investigation of their potential roles in HCV infection.
Proteasome activator PA28γ regulates Core degradation and plays a critical role in HCV pathogenesis and is thus, a promising target for anti-HCV therapies. Suppressed PA28γ expression in transgenic mice expressing Core in the liver, impairs HCV pathogenesis. However, a precise understanding of the role of PA28γ in HCV pathogenesis remains unclear. In order to study the role of PA28γ involving in the biological network, differentially expressed genes by comparing Core transgenic mice with or without the knockout of PA28γ expression against the wild type (WT) samples were identified using protein array. The differentially expressed proteins were then integrated with the human PPIs to establish extended PPI networks using TargetMine. TargetMine was also employed for functional analysis of the inferred PPI networks to identify cellular processes targeted by Core and PA28γ in HCV pathology and prioritize candidates for further experimental investigation of their potential roles in HCV infection.
Reference:
- Tripathi LP, et al. (2012) Proteomic Analysis of Hepatitis C Virus (HCV) Core Protein Transfection and Host Regulator PA28γ Knockout in HCV Pathogenesis: A Network-Based Study. J Proteome Res. 11: 3664-3679. [PubMed:22646850]